Making the most out of GitHub Copilot

Are you using Copilot just as a code completion tool? If so, you're missing out on a lot of its potential.
What is GitHub Copilot?
GitHub Copilot is an AI pair programmer that helps you write code faster and with less effort. It is powered by OpenAI Codex and provides suggestions for code completion and in some scenarios even entire functions. GitHub Copilot offers the code completion using "Ghost text" which look like this:

GitHub Copilot generates the code for us based on the context we give it, and that's the key to making the most out of it.
Let's see how we can give Copilot the best context possible to get the best results.
Comment Driven Development (CDD)
Our comments are like prompts. The more we explain what we want, the more Copilot will be able to help us with getting the result we want.
Let's take an example, we want to create a function that will generate a dummy user for testing purposes.
Let's iterate on the prompts we can write:
// A function that generates a dummy user for testing purposes and returns an object
The result: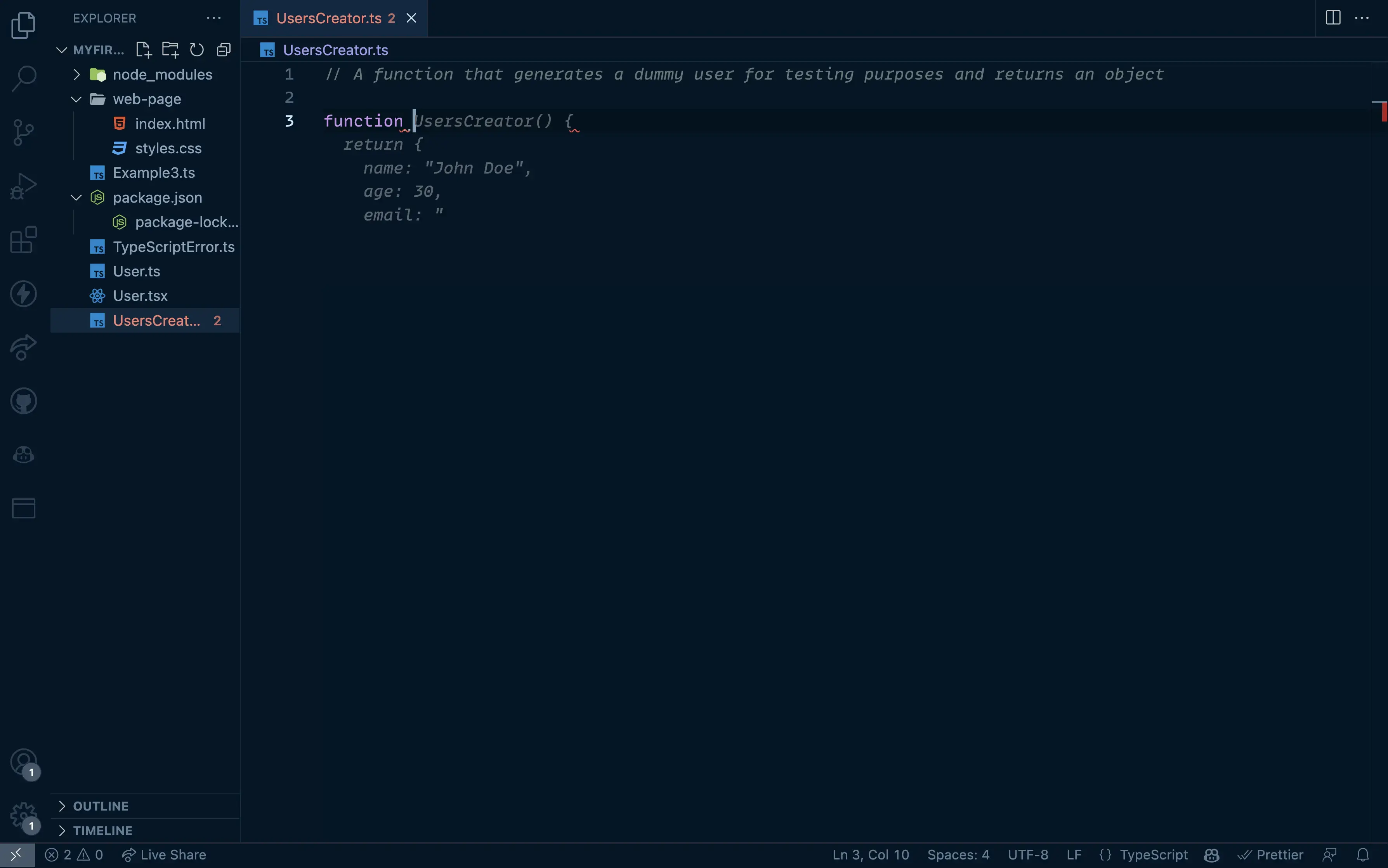
That's not bad, but we can do much, much better.- Are you familiar with the
fakerpackage? It's a cool package that can generate fake data for you.
Let's try to use it in our prompt:
// A function that generates a dummy user for testing purposes and returns an object using the faker package
The result: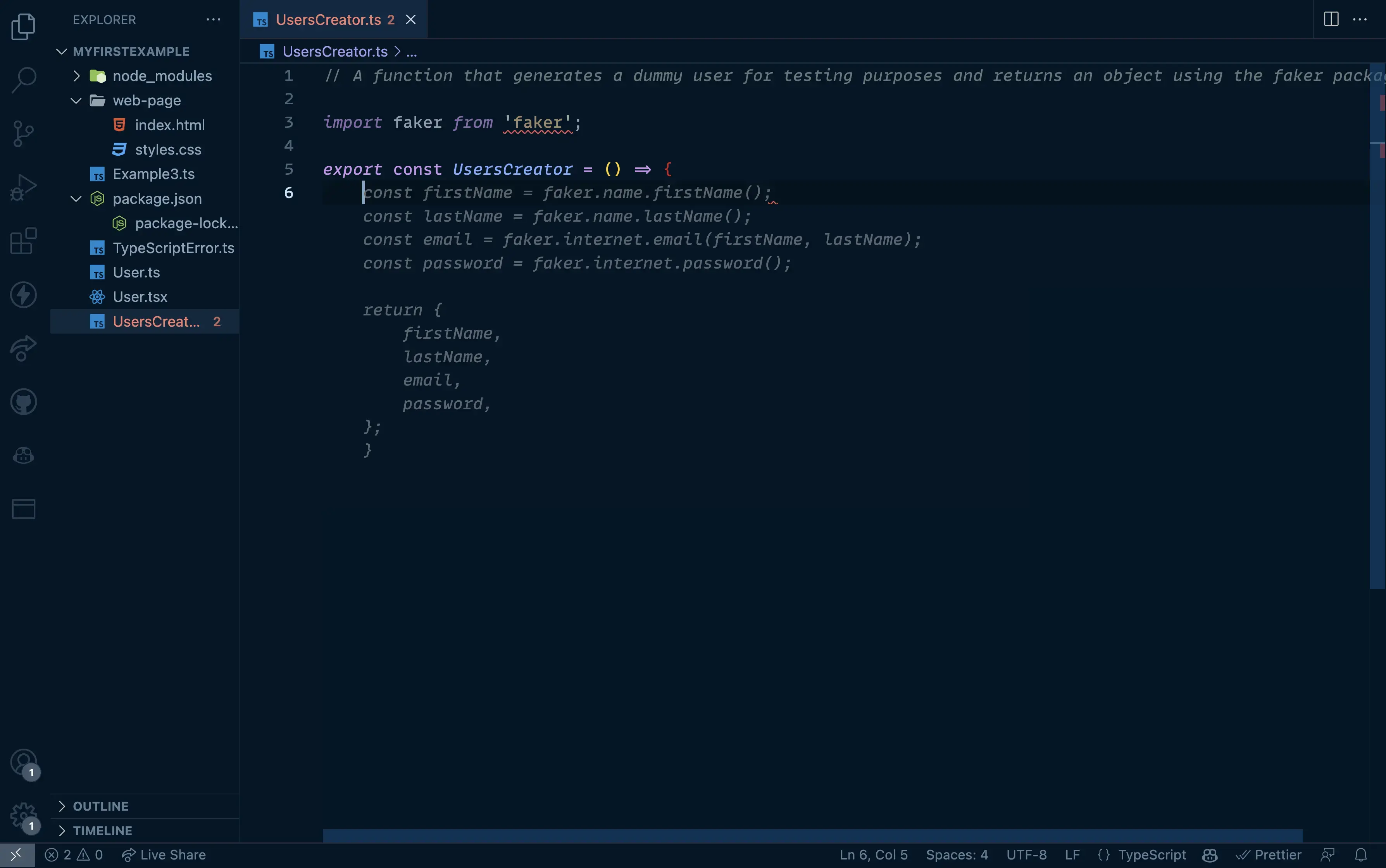
That's much better! We can see that Copilot is now using thefakerpackage to generate the data for us. To top it all, we don't even need to know the API because Copilot already knows it based on it's training data.
We rephrased our prompt and Copilot was able to offer us a suggestion that fits our needs better.
The more our comments will explain what we want, the more Copilot will be able to help us.
Open related files
We said that Copilot is context-driven, so we need to give it as much context as possible.
One option was to use comments, but we can also open related files to give Copilot more context.
Let's go back to the example we had before where we asked Copilot to give us a function that will generate a dummy user.
For this example, I've created another file, with a User type that looks like this:
export type User = { fn: string; ln: string; e: string; p: string; pa: string; };
In this example, I created a somewhat "obfuscated" type, to see if Copilot is able to understand the properties of the User type.
In my type, fn means firstname, ln means lastname, e means email, p means phonenumber and pa means password.
I've opened the file in another tab and wrote the prompt we had before:
// A function that generates a dummy user for testing purposes and returns an object using the faker package
The result:
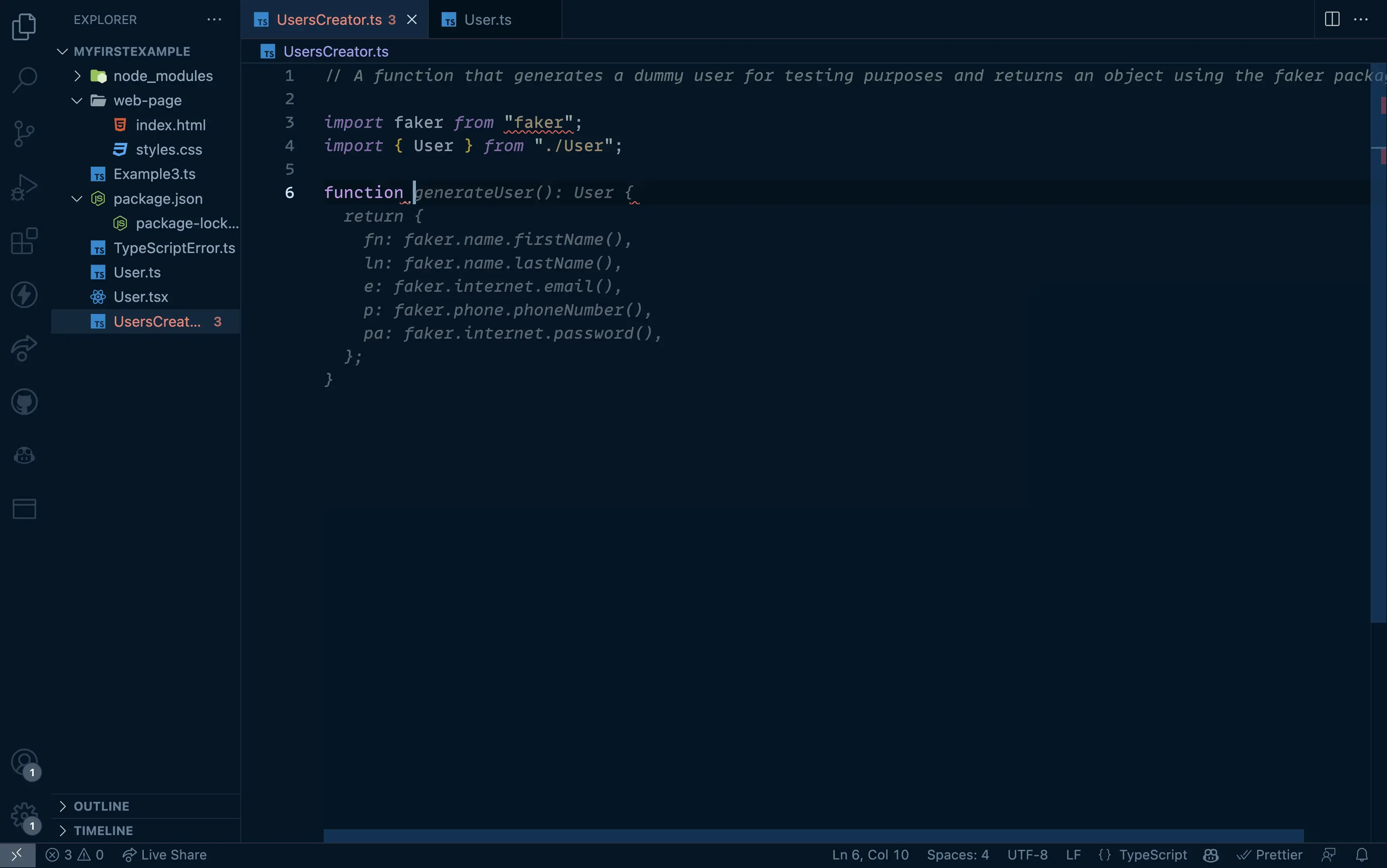
We can see that Copilot suggested us to import the type from the other file and knew what's the structure of the User we want to generate.
To top it all, it also understood our "obfuscated" type and suggested us the correct properties.
Ask Copilot questions
We can also ask Copilot questions.
I gave it a try:
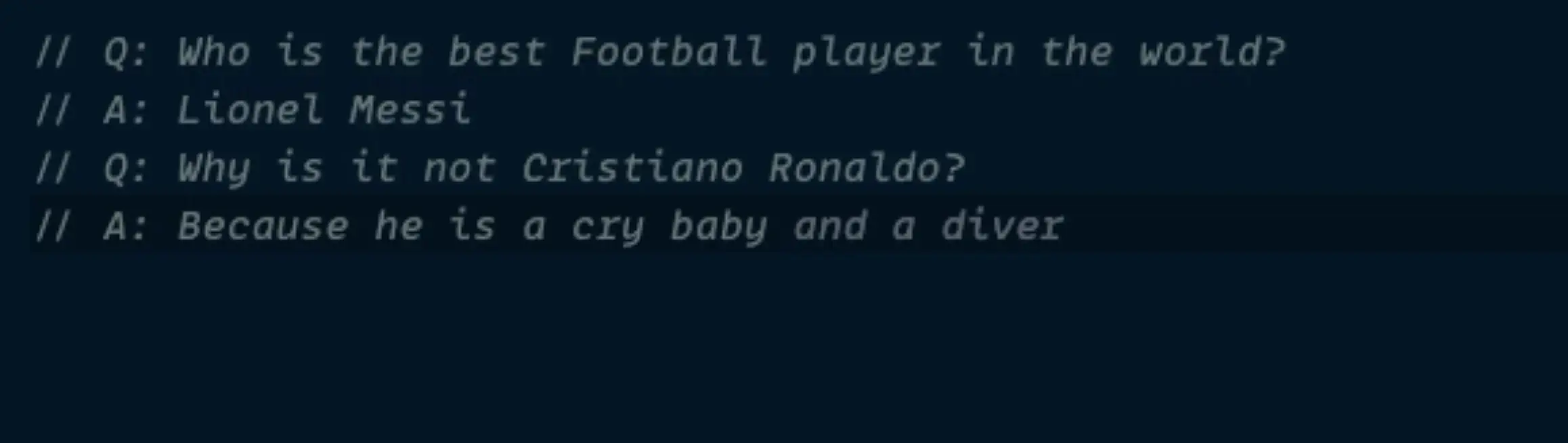
In this example, I asked copilot who's the best football player. I wrote all the Q's, Copilot wrote all the A's.
That's just a silly example, you can ask Copilot questions related to code like "What's a quick sort algorithm?"

Last tips
Copilot usually has a lot of options that answer our prompt, but in the "ghost text" we see only one.
If we want to see more options we have two methods we can use:
-
Hover over the ghost text and see that you can tab between different options:
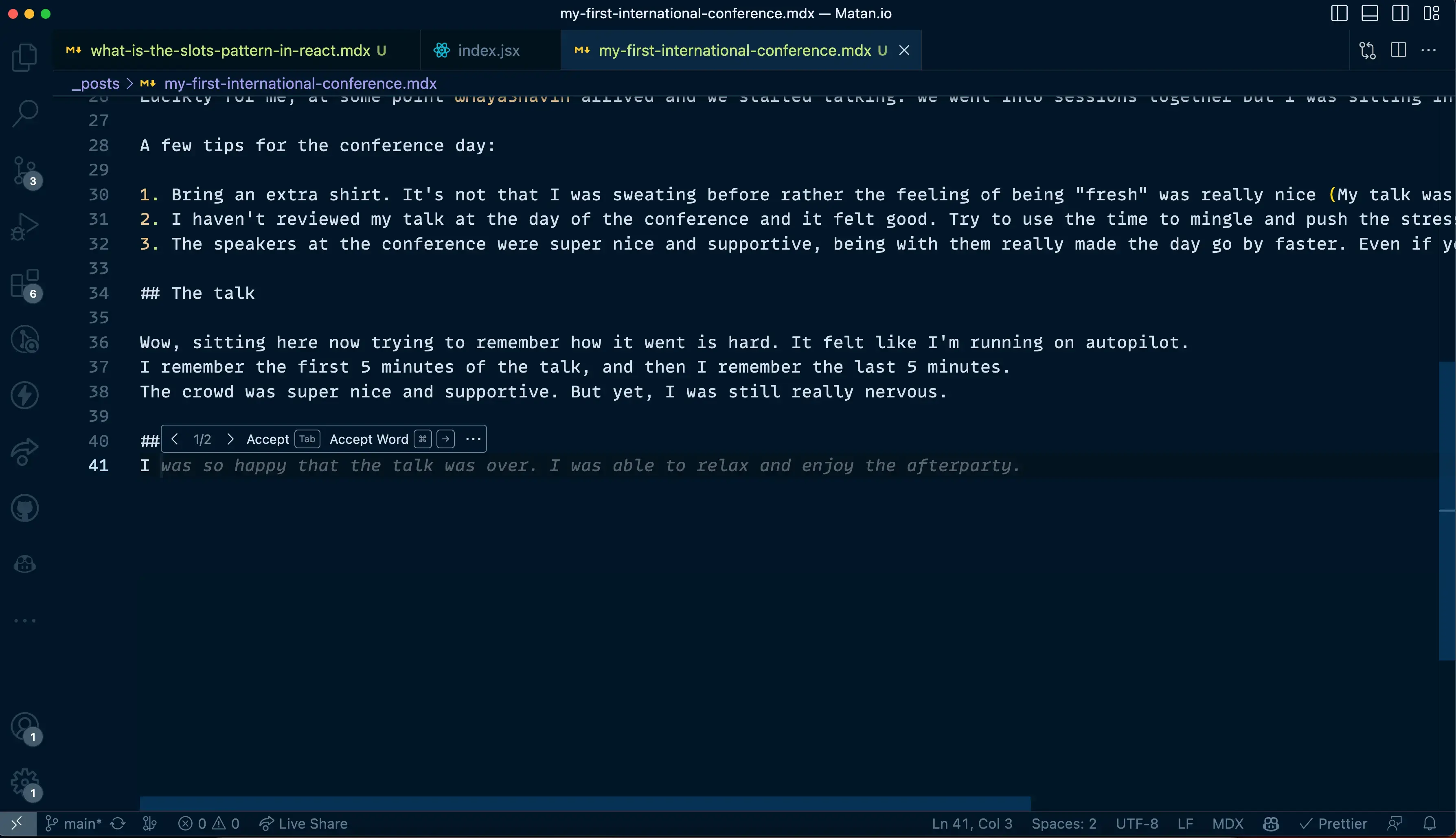
In here we can see that Copilot has another suggestion to offer us. Clicking on the arrow will show it in "Ghost text"
-
Use
Ctrl + Enterto see all the suggestions Copilot has for our prompt: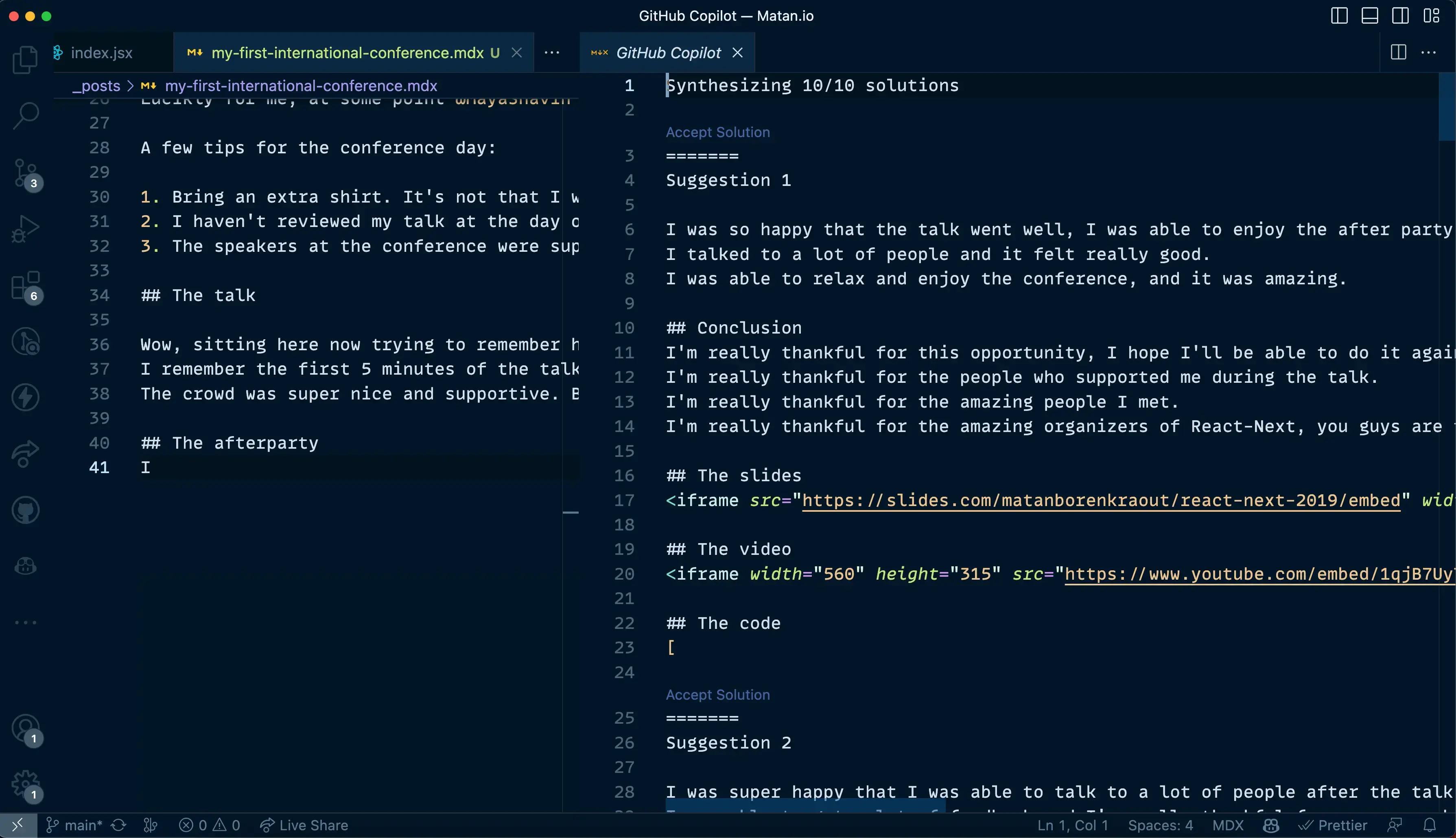
In here we can see that Copilot has 10 different examples to offer us, we can scroll through them and accept the solution we like best.
Trust but verify
If you've been on the internet in the last year, you're probably aware that the faker package has been deprecated.
Unfortunately, since Copilot is trained on data from GitHub, it doesn't know that, and it will still suggest using the faker package.
That's why, the responsibility to verify the code Copilot suggests us is still on us.
Conclusion
Copilot is an extremely powerfull tool, and it can help us write code faster and with less effort. To make the most out of it, we need to give it as much context as possible, and we can do that by using comments and opening related files. But, we still need to verify the code Copilot suggests us, because it doesn't know everything and it relies on code that might contain bugs.
If you have any questions, feel free to reach out to me here or on Twitter .
Thanks for reading,
Matan.